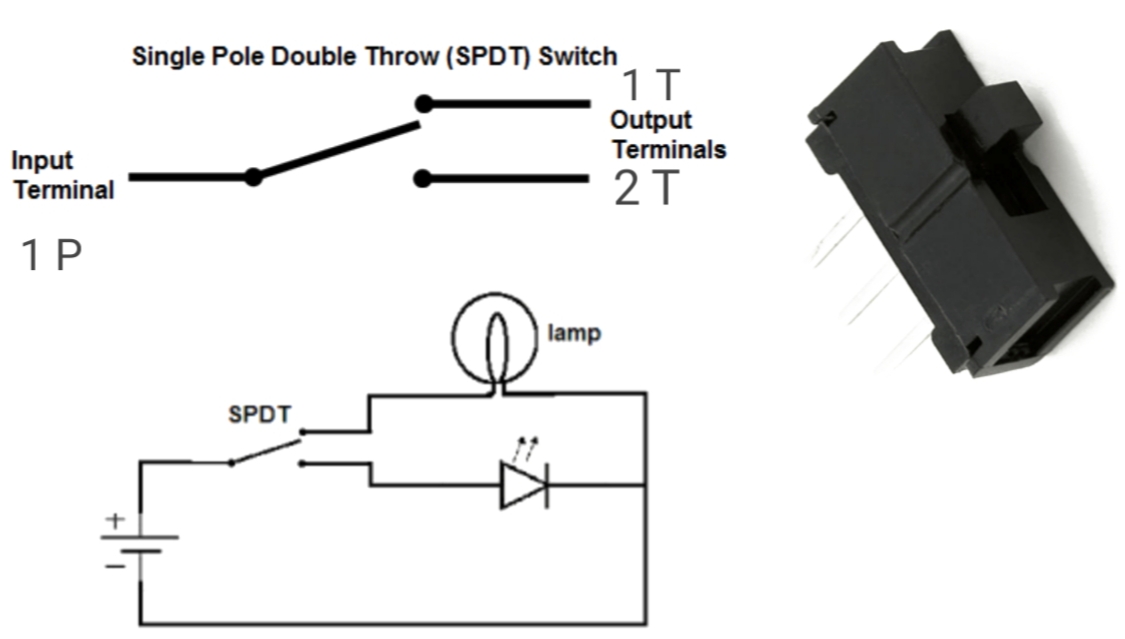
Imagine having the power to effortlessly divert electrical flow between two different circuits with a flick of a switch. This is the essence of the Single-Pole Double-Throw (SPDT), often referred to as the "on-on" switch. Its ingenious design allows for a single input to be connected to one of two outputs, making it a fundamental component in countless electrical applications. This article will delve into the world of SPDT on-on switches, exploring their functionality, benefits, and practical uses.
The SPDT switch's simplicity belies its versatility. Unlike a simple on-off switch, the SPDT offers a choice. It's like a railway switch, directing the electrical current down one track or another. This seemingly small difference opens up a world of possibilities, from controlling multiple lights with a single switch to complex circuit configurations in industrial settings.
While the exact origins of the SPDT switch are difficult to pinpoint, its development is closely tied to the advancement of electrical engineering in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. As electrical systems became more complex, the need for versatile switching mechanisms grew, leading to the creation of the SPDT and other switch types. The SPDT switch's importance stems from its ability to simplify complex wiring and provide flexible control over electrical circuits.
A common issue with SPDT switches, like any electromechanical device, is contact wear. Over time, repeated use can lead to degradation of the internal contacts, resulting in intermittent connections or complete switch failure. Proper selection and maintenance are essential for long-term reliability.
Understanding the terminology associated with SPDT switches is crucial. "Single-pole" signifies that the switch controls a single circuit. "Double-throw" indicates the switch can connect to two different outputs. The "on-on" designation clarifies that the switch has two "on" positions, meaning the input is always connected to one output or the other. There's never a completely "off" state where the input is disconnected from both outputs.
A simple example of an SPDT switch application is controlling two lights with one switch. Flipping the switch one way turns on the first light, while flipping it the other way turns on the second. Another common use is in A/B switching for audio signals, allowing users to select between two different audio sources.
One benefit of SPDT switches is their ability to simplify wiring. Instead of running separate wires for each output, a single SPDT switch can manage multiple connections. This reduces complexity and can save on wiring costs. Another advantage is enhanced control, enabling users to select between different circuits or devices with ease. Lastly, their compact size makes them ideal for applications where space is limited.
Implementing an SPDT switch effectively involves careful planning and execution. First, identify the specific application and the circuits involved. Next, select an appropriate SPDT switch rated for the voltage and current of the circuit. Finally, wire the switch according to the circuit diagram, ensuring proper connections to the input and both outputs. Testing the circuit thoroughly after installation is crucial to ensure proper operation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of SPDT On-On Switches
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simplified Wiring | Potential for Contact Wear |
| Enhanced Control | No True "Off" State in On-On Configuration |
| Compact Size | Can be Confusing for Some Users |
Five best practices for implementing SPDT switches include: 1) choosing the correct switch rating, 2) using a clear wiring diagram, 3) securing all connections, 4) testing the circuit thoroughly, and 5) using appropriate enclosures for safety.
Five real-world examples of SPDT on-on switch applications are: controlling two lights with one switch, A/B switching for audio, selecting between two different power sources, reversing the polarity of a motor, and switching between different antenna inputs.
Five challenges related to SPDT switches and their solutions include contact wear (replace the switch), incorrect wiring (consult a wiring diagram), overheating (use a higher-rated switch), intermittent connections (clean the contacts), and switch failure (replace the switch).
Frequently Asked Questions: 1) What does SPDT stand for? (Single-Pole Double-Throw) 2) What is an on-on switch? (A switch with two "on" positions) 3) How does an SPDT switch work? (It connects one input to one of two outputs) 4) What are the applications of SPDT switches? (Controlling lights, A/B switching, etc.) 5) How do I wire an SPDT switch? (Consult a wiring diagram) 6) How do I troubleshoot an SPDT switch? (Check connections, replace if necessary) 7) What are the benefits of SPDT switches? (Simplified wiring, enhanced control) 8) What are the common issues with SPDT switches? (Contact wear)
Tips and tricks for working with SPDT switches include using a multimeter to test continuity and ensuring all connections are secure.
In conclusion, the SPDT on-on switch is a versatile and essential component in a wide range of electrical applications. Its ability to selectively connect a single input to one of two outputs simplifies wiring and provides enhanced control. From simple household lighting to complex industrial systems, the SPDT switch plays a critical role. Understanding its functionality, benefits, and best practices is crucial for anyone working with electrical circuits. While challenges like contact wear can arise, proper selection, implementation, and maintenance ensure the long-term reliability and effectiveness of SPDT switches. By mastering the nuances of this seemingly simple device, you unlock a powerful tool for controlling and manipulating electrical flow.
Unleash the beast exploring the chevy 2500hd duramax powerhouse
Decoding march madness first round predictions
Unlocking the secrets of sherwin williams popular gray reviews and insights